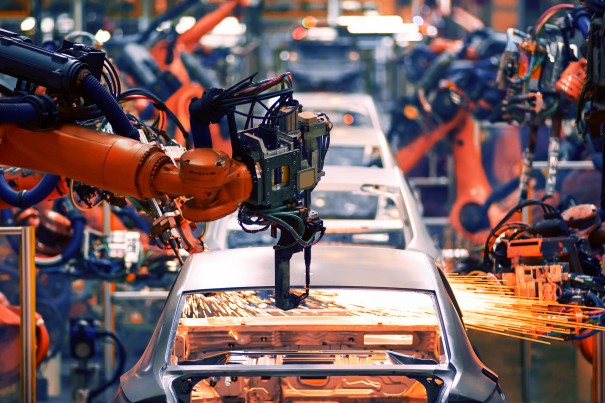
Dual-phase steel for cold forming: tailored portfolio for modern lightweight construction
High strength, excellent formability and enhanced crash performance: The specific requirements for the different applications in automotive engineering can be enhanced with our tailored and needs-oriented portfolio of cold-rolled dual-phase steels. A coordinated range that is optimally tailored to the component function and customer application.
Manganese-boron steels and AS Pro coating for hot forming: Highest strength with good forming properties
For hot forming thyssenkrupp supplies hot-rolled, cold-rolled and coated MBW® manganese-boron steels. A newcomer to the range: AS Pro, the innovative coating for significantly improved component and process reliability in automotive engineering.
In the automotive industry MBW® manganese-boron steels are mainly used for safety-relevant structural parts. Our MBW® steels offer extremely high strengths after hot forming while retaining very good forming properties.

thyssenkrupp Steel pursues a technology-open approach in the manufacture of lightweight steels: For both cold and hot forming, customers have access to comprehensive portfolios that support sustainable component production.
Public perception of industrial processes is not always unprejudiced. A current example of this is the discussion that has arisen about the hot forming process, since it requires heating materials to temperatures of 900 degrees Celsius and more. At first glance, this sounds like high energy consumption and high CO2 emissions – and thus not very sustainable. However, looking at the procedure in terms of the application often reveals a different situation. Hardly anyone knows this better than Thomas Flöth from the New Applications department at thyssenkrupp Steel. "There are good reasons to use both cold and hot forming, depending on the application," says the engineer, referring to the individual requirements in component production. "In the automotive sector, it's often a matter of getting as much as possible out of lightweight construction. Here, depending on the task, hot forming can also save quite a lot of material – and thus also CO2." Another aspect for saving material is the material utilization factor, where hot forming also tends to offer advantages over cold forming.
Lightweight steel: the less weight, the better
Particularly when it comes to the life cycle assessment of forming processes, internal studies at thyssenkrupp Steel have revealed that material reductions are decisive. Thomas Flöth: "The studies we've done show very clearly: It's not so much the manufacturing process that matters, but rather the weight and material utilization of the subsequent component: the lower the component weight and the better the material utilization, the more sustainable." He is convinced that the method associated with the forming process will exert an even more marginal influence in considerations of sustainability in the future, and all the more so when heating processes are decarbonized through the use of green electricity or hydrogen. Following the guiding principle "The most environmentally friendly material is the one that doesn't have to be produced in the first place" – after all, lightweight construction reduces the amount of material used in a component for the same performance, and less steel has to be produced – thyssenkrupp Steel pursues a technology-open strategy: in each individual case, we carefully examine which material and which process are optimally suited to the respective field of application.
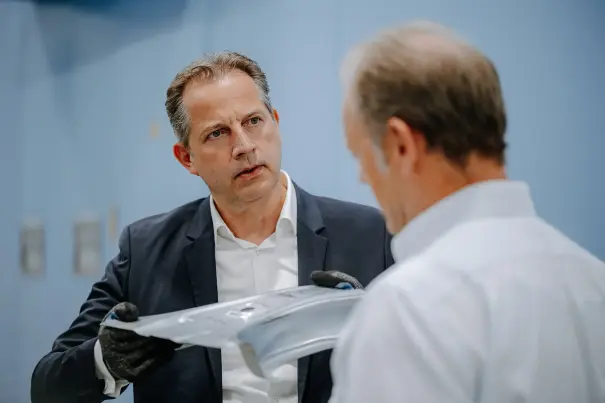

If a component has to be able to absorb a particularly large amount of energy in a crash, as is the case with a front longitudinal member, for example, cold-formed highest-strength AHSS materials such as jetQ® 980 and jetQ® 1180 are ideal thanks to their outstanding ductility. These latest-generation modern multiphase steels are ready for series production now, and they are currently undergoing the approval process at various OEMs. "The initial feedback from our customers on processing is very positive," reports Dr. Patrick Kuhn, product manager for multiphase steels at thyssenkrupp Steel.
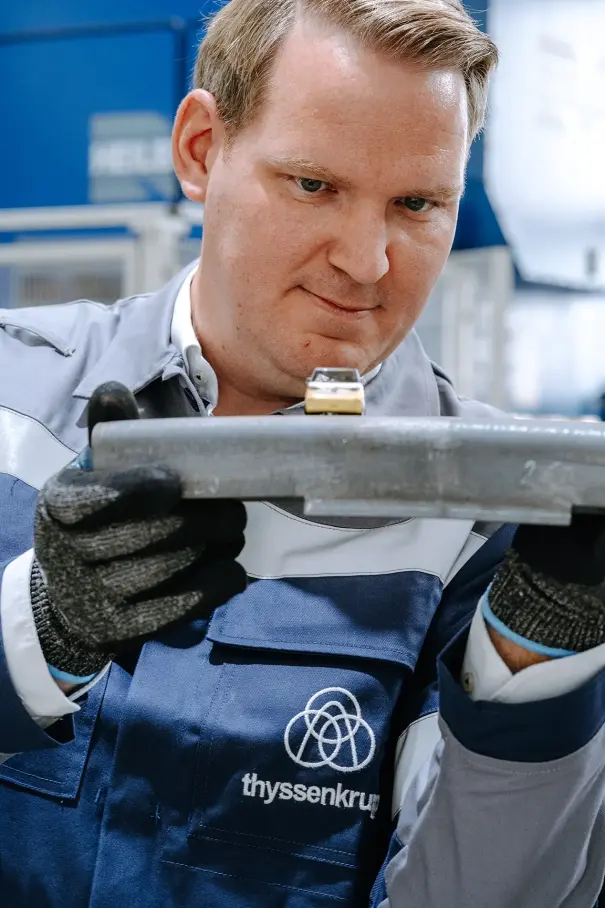

jetQ® grades also perform well in terms of resistance to deformation, while highest-strength hot-forming steels such as MBW® 1500 or MBW® 1900 show even better performance here: for example, when used in safety-relevant body components such as B-pillars, which must neither deform significantly in an accident nor, in the worst case, fail. However, ductility is now also a major issue in hot forming – with MBW® 1200, the strength is moderately reduced in favor of increased ductility. "These properties also impressed Volkswagen so much that the material is being used alongside other hot forming grades to build the new all-electric VW ID Buzz," explains Georg Parma, thyssenkrupp Steel's product manager for hot forming.
Material selection depends on many factors
The automotive industry will continue to require a balanced mix of cold- and hot-formed steels in the future, and in terms of competition with lightweight body materials, steel is therefore hardly likely to surrender its dominant position in the coming years. "The question of balancing the respective proportions of cold and hot forming depends not least on the carmaker's highly individual material concept. In essence, however, the respective component requirements determine the use of technology," says Thomas Flöth, summarizing the situation for OEMs. Until now, lightweight construction has primarily been an issue of reducing fuel consumption and emissions in vehicles running on conventional fossil fuels. However, against the backdrop of locally emission-free electric mobility, the sustainability focus is shifting from the use phase to the production phase. Lightweight construction therefore remains an important issue – the requirements for crash safety (for example the protection of the battery) are even increasing in the case of electric cars. For this reason, thyssenkrupp Steel will continue to invest in developing new lightweight steels with improved material properties – both for cold and hot forming.

Whether microalloyed steels for suspension and axle applications, high-strength multi-phase steels for single-skin control arms, or application-optimized manganese-boron steels for precision steel tubular applications such as stabilizers, thyssenkrupp Steel offers an extensive hot-rolled portfolio for the cost-effective lightweighting of high-strength chassis components.
Our hot-rolled chassis materials are available as uncoated and coated hot wide strip and slit strip and as uncoated precision strip, on request also as slit coil.

Front and rear seats must meet the highest demands in terms of cost-effectiveness, installation space, lightweight design, safety, and comfort.
thyssenkrupp Steel offers a tailored portfolio for cost-effective lightweight steel seat structures: From highly ductile hot-rolled strip and precision strip with tight tolerances to microalloyed cold-forming steels and cold-rolled high-strength multi-phase steels – with best forming and joining properties.
Click here for details of lightweight steels for seat structures
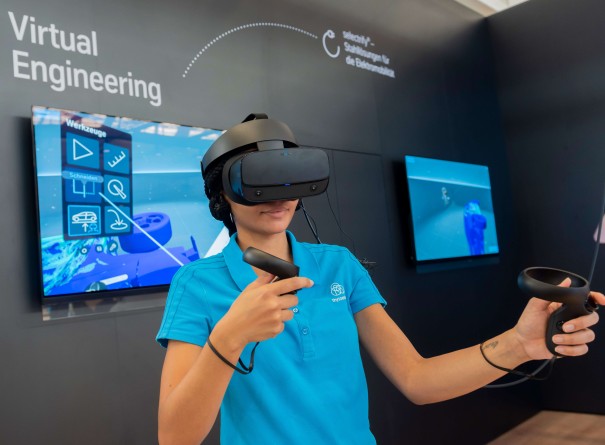

Research and development of new steel materials and technologies
Our Application Technology Center has been helping customers with innovative solutions to get the most out of their steel for 50 years.
The name says it all: as thyssenkrupp Steel’s innovation lab,the Application Technology Center aims to do more than simply research, develop, and manufacture new steel materials and technologies – it also strives to ensure that the company’s customers get the most out of these developments.
















